Can CBD make you high? The answers is no, and here’s why.
You might have heard of THC, the intoxicating cannabinoid that gives cannabis its distinctive “high”, but what about its sister CBD? Can CBD make you high?
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is one of the main active cannabinoids found in cannabis, alongside cannabidiol (CBD). Both of these cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system to induce a range of effects on the body. However, these two cannabinoids differ in terms of their intoxicating effects, structure, and receptors. Let’s take a look at these to find out why they cause different effects.
Why Does THC Have Intoxicating Effects?
THC is well-known for its intoxicating abilities. The lower the THC content, the less intoxicating the cannabis will be. But what makes THC so intoxicating?
One big factor is its activation of cannabinoid receptors.
THC acts on the G-protein coupled receptors CB1 and CB2. Researchers believe that THC’s activation of CB1 might play a role in creating its trademark intoxicating high.

One study from 2001 used a CB1 antagonist to block the activation of CB1 through THC. Participants in the study received either the CB1 blocker or a placebo, two hours before smoking a joint with 2.64 percent THC. Researchers wanted to investigate how THC might affect the body without access to the CB1 receptor. The results showed that participants who received the CB1 blocker felt a significant reduction in cannabis intoxication. This reduction also seemed to be dose-dependent, with a 90mg dose of the blocker producing a 38-43 percent reduction in intoxication self-assessments. This indicates that the CB1 receptor plays a key role in facilitating THC’s intoxicating effects.
THC, Brain Function, and Reward Behavior
So we know one of the pathways through which THC might induce its high, but what does it then do to the brain? One study published in Psychological Medicine sought to answer this question. Researchers used neuroimaging to analyze the effects of cannabis consumption on brain structure and function.
The review looked at forty-one studies and found that THC and cannabis consumption resulted in an increase in resting activity. It also caused activation of the anterior and frontal cingulate cortex regions of the brain during cognitive tasks. The results suggest that THC may modulate the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in complex behaviors and can control planning, judgment, and personality development.
Another key component of THC’s intoxicating effect is how it acts on the reward system. An increase in certain neurotransmitters, like serotonin, can induce a positive feeling that might contribute to the intoxicating symptoms of THC.
The presynaptic terminal is hyperpolarized when THC binds to the CB1 receptor. This closes calcium channels and holds back inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters at their synapses. The response may then modulate the release of neurotransmitters that induce feelings of euphoria, such as serotonin.
Can CBD Make you High?
Some might associate CBD with a high because it can be found in cannabis plants that also contain THC. However, this cannabinoid cannot get you high. But why not?
That mainly comes down to two key differences between CBD and THC: their structure and the receptors to which these compounds bind.
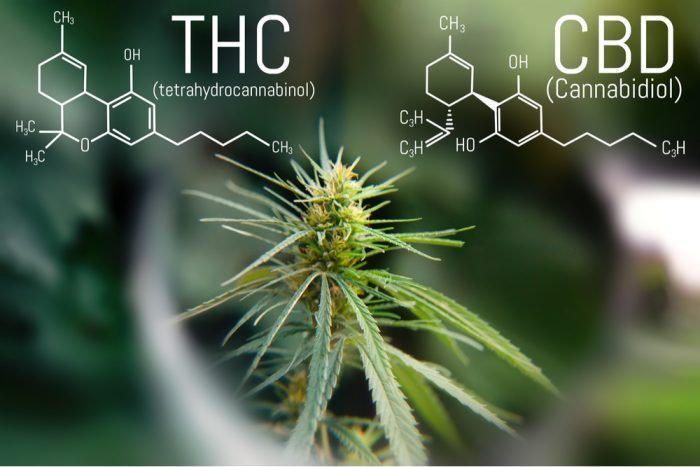
CBD and THC look very similar at the molecular level. In fact, they even have the same molecular formula of C21H30O2. However, these two cannabinoids have one distinct difference that sets them apart: THC contains a cyclic ring, while CBD has a hydroxyl group. This may not mean much to those unfamiliar with chemistry, but this difference is key in deciding what effects both of these compounds cause.
Moreover, while THC binds to the CB1 receptor, which has been shown to play a crucial role in inducing a high, CBD doesn’t directly activate any cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it acts on non-cannabinoid receptors and modulates receptor pathways.
CBD May Actually Counteract the Effects of THC
It turns out that CBD might actually reduce THC’s psychogenic effects. One study published in Journal of Psychopharmacology found that when participants were given CBD before consuming THC-rich cannabis, the participants felt reduced levels of paranoia and psychotic symptoms, and improved memory skills. This indicates that CBD might be able to block the cognitive effects of THC.
Another study in Neuropsychopharmacology used MRI to investigate the different effects of THC and CBD on the brain. It found that the two cannabinoids actually induce the opposite effects on regional brain function, which might explain how CBD may be able to block the intoxicating effects of THC.

Good Sources of CBD
With all this substantial evidence indicating that CBD doesn’t induce a high, CBD products seem to be a safe option for those wanting to consume cannabis without any of the intoxicating effects.
There are a variety of forms and methods for consuming CBD, including flower. Some cannabis plants have richer concentrations of CBD and lower THC levels.
There are also CBD concentrate products that only contain CBD, including:
- Shatter – Resembling glass, as the name suggests it can shatter or snap. Ideal for vaporizing and dabbing.
- Wax – Consistency of candle wax, ideal for vaporizing and dabbing.
- Budder – Frosting-like and viscous in texture, ideal for adding to a cannabis joint.
- Crumble – A drier form of budder, easier to handle, and ideal for dabbing or smoking.
- Oil – Refined oil, ideal for vaporizing, ingestion, and edibles.
There’s no denying that cannabis has medicinal value. But, not every condition needs the effects of THC in order to achieve its therapeutic effects. If you’re in a workplace with regular drug testing, or if you have to operate machinery, CBD may be a better option for you. After all, it provides plenty of benefits and none of the high.





